Natural Inflation Hedge
Returns aren’t the only attraction. Timberlands’ intrinsic and proven long-term ability to preserve capital by historically tracking the consumer-price index, can serve as an effective inflation hedge.
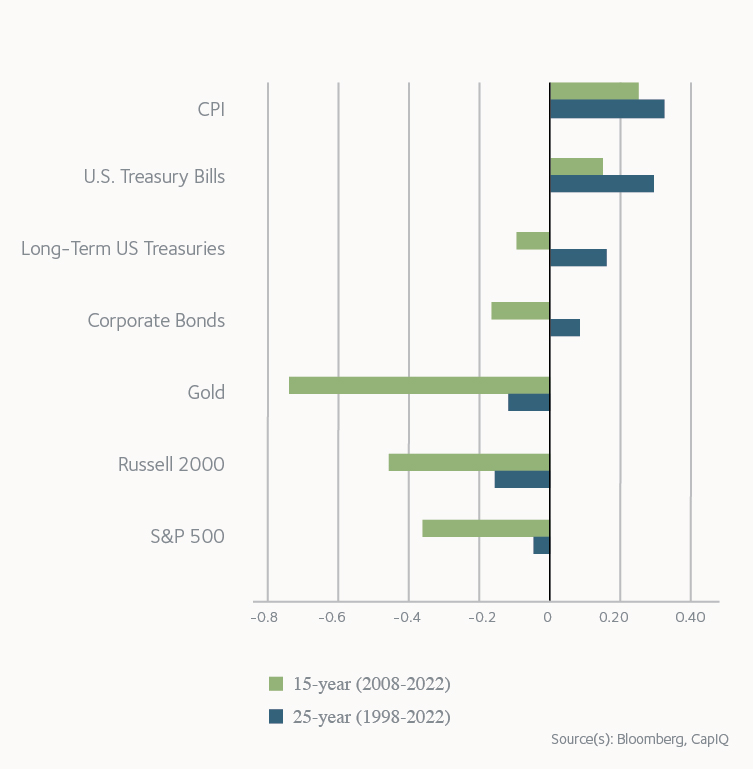
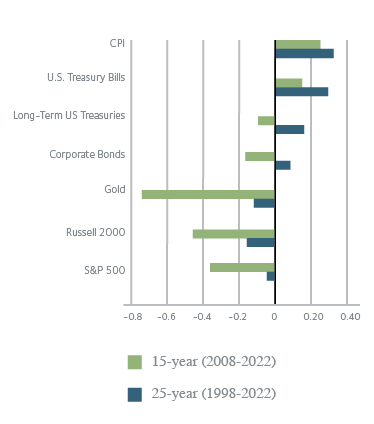
Timberland Correlation vs Inflation
Timberland has historically maintained a positive correlation with unanticipated spikes in inflation. During periods of high inflation, as in the 1970s, timberland provided a partial inflation hedge by producing a correlation coefficient of 0.34 through the decade. More recently, U.S. timberland followed inflation with a correlation of 0.93 from 2018 through 2022. In most cases, timber prices rise with inflation and account for a larger proportion of timberland returns than would otherwise be expected.
During periods of disinflation or low inflation, timberland’s annual correlation to CPI typically declines or becomes negative. Biological growth, as a physical process that is entirely unrelated to economics, accounts for a higher proportion of timberland returns during a low inflation environment.
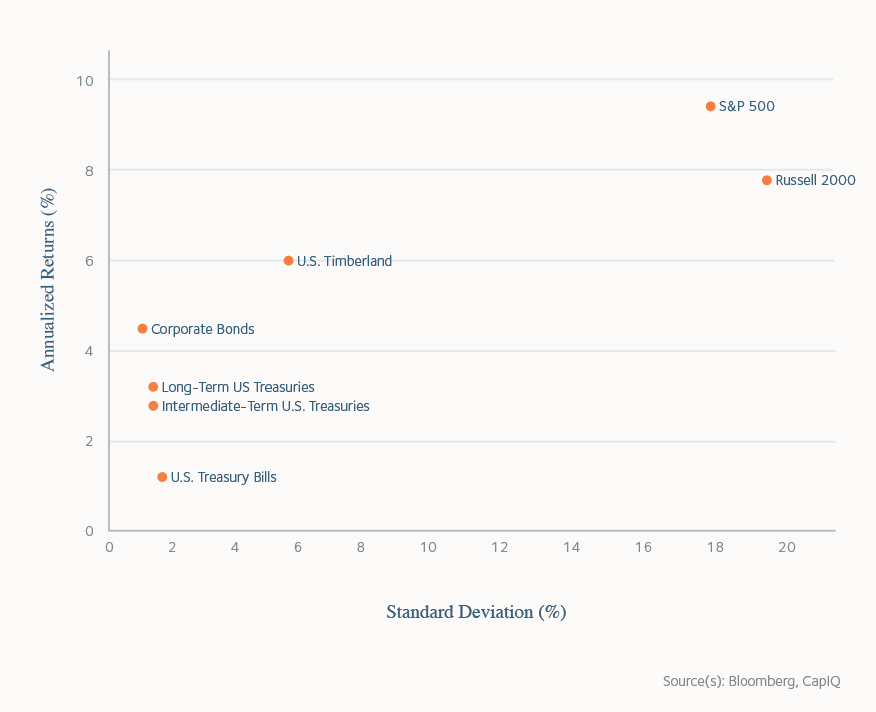
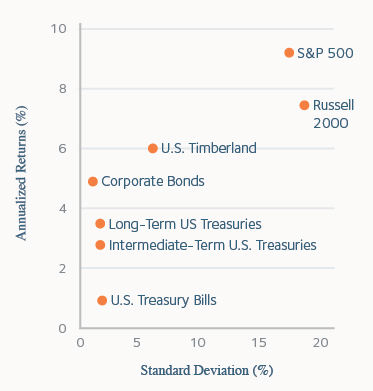
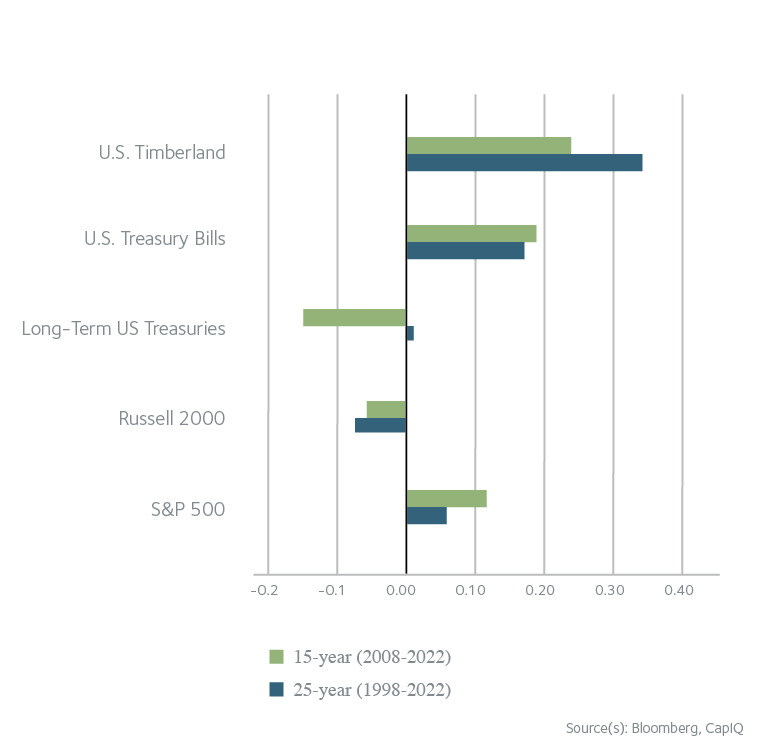
However, timberland’s inflation hedging potential becomes most evident when applied to longer investment periods which are typical for the asset class. As an example, rolling 10-year returns for U.S. timberland investments from 1997 to 2022 had a high correlation (0.85) to changes in average annual inflation over those same 10-year periods. Increasing the investment period only tightens the relationship. For comparison, the S&P 500 and Russell 2000 produced correlation coefficients of 0.11 and 0.30 relative to inflation over the same period of rolling 10-year returns.